Introduction to Angkor Wat
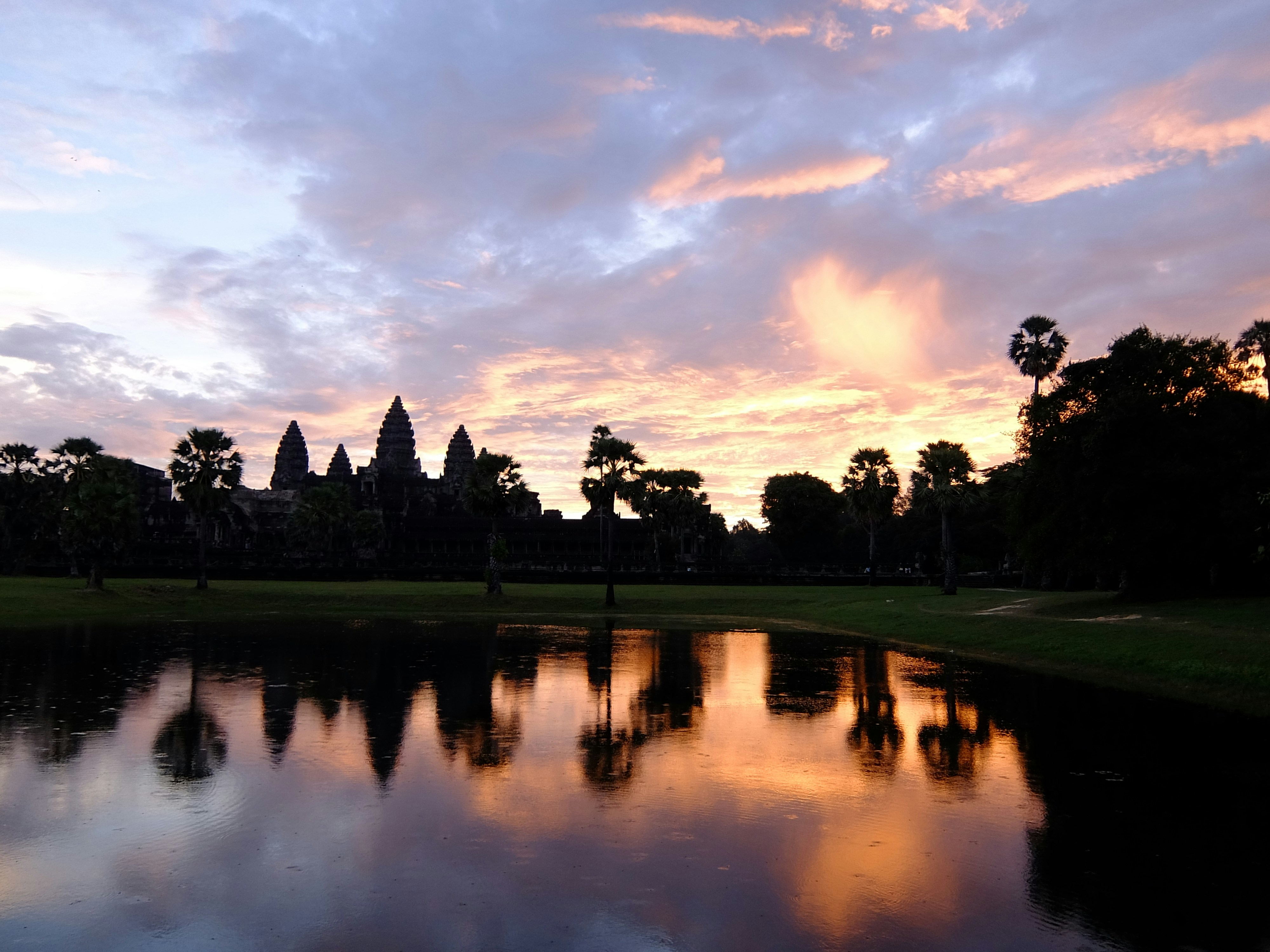
Angkor Wat, located in Cambodia, is one of the most remarkable architectural achievements in history. Originally constructed in the early 12th century as a Hindu temple dedicated to the god Vishnu, it later transformed into a Buddhist temple, reflecting the dynamic spiritual history of the region. Its grandeur and intricacy stand as a testament to the artistic capabilities of its builders.
The Architectural Marvel
The design of Angkor Wat is a prime example of classical Khmer architecture, featuring an extensive layout that covers over162 hectares. The temple complex is characterized by its moat and outer walls, which beautifully encase the central tower representing Mount Meru, the axis of the universe in Hindu cosmology. The detailed bas-reliefs showcasing different stories from Hindu mythology, along with the precise alignment of the structure to the rising sun, signify the advanced knowledge of the ancient builders.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Angkor Wat is not only a national treasure of Cambodia but also a symbol of its identity. Declared a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1992, it attracts millions of visitors every year, eager to experience the rich history and spiritual essence it embodies. The temple is a place where the beauty of nature meets the creativity of mankind, making it a cherished destination for historians, architects, and travelers alike.